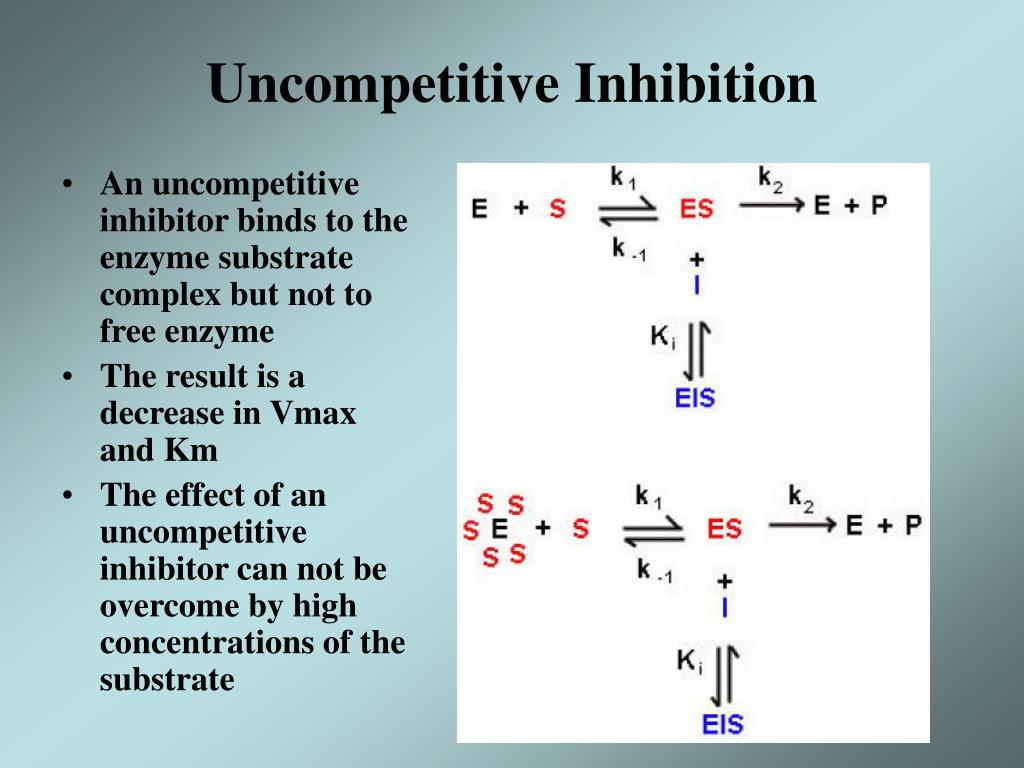
Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant . Web the inhibitor constant, ki, is an indication of how potent an inhibitor is; Web in another somewhat rare form of noncompetititve inhibition called uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor. Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept of the double reciprocal plot. A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant k’ i in scheme 2, do not bind to the free enzyme. It is the concentration required to produce half maximum inhibition. Web k ii is also named kiu, where the subscript u stands for the uncompetitive inhibition constant. A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as s.
from www.slideserve.com
Web k ii is also named kiu, where the subscript u stands for the uncompetitive inhibition constant. It is the concentration required to produce half maximum inhibition. A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as s. Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant k’ i in scheme 2, do not bind to the free enzyme. Web in another somewhat rare form of noncompetititve inhibition called uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor. Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept of the double reciprocal plot. A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. Web the inhibitor constant, ki, is an indication of how potent an inhibitor is;
PPT Enzyme PowerPoint Presentation ID305372
Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as s. A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant k’ i in scheme 2, do not bind to the free enzyme. Web in another somewhat rare form of noncompetititve inhibition called uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor. Web k ii is also named kiu, where the subscript u stands for the uncompetitive inhibition constant. A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as s. It is the concentration required to produce half maximum inhibition. Web the inhibitor constant, ki, is an indication of how potent an inhibitor is; Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept of the double reciprocal plot.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT CHMI 2227E Biochemistry I PowerPoint Presentation, free download Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept of the double reciprocal plot. Web k ii is also named kiu, where the subscript u stands for the uncompetitive inhibition constant. It is the concentration required to produce half maximum inhibition. Web the inhibitor constant, ki, is an indication of how potent an inhibitor is;. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From wahlm.com
The difference between Ki, Kd, IC50, and EC50 values (2023) Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant It is the concentration required to produce half maximum inhibition. Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant k’ i in scheme 2, do not bind to the free enzyme. A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From www.lecturio.com
Enzyme Inhibition Concise Medical Knowledge Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept of the double reciprocal plot. Web the inhibitor constant, ki, is an indication of how potent an inhibitor is; A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. A look at the top mechanism shows that in. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From biology.stackexchange.com
biochemistry Why does inhibition decrease the Michaelis Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant k’ i in scheme 2, do not bind to the free enzyme. A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. It is the concentration required to produce half maximum inhibition. A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From www.youtube.com
inhibition YouTube Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. Web k ii is also named kiu, where the subscript u stands for the uncompetitive inhibition constant. Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant k’ i in scheme 2, do not bind to the free enzyme. A look at the top. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From in.pinterest.com
inhibition Definitions, Enzymes, Type Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web in another somewhat rare form of noncompetititve inhibition called uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor. A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as s. It is the concentration required to produce half maximum inhibition. Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant k’ i in scheme 2, do not bind to the free enzyme. Web. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 12 Enzyme Inhibition, and Control PowerPoint Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web in another somewhat rare form of noncompetititve inhibition called uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor. Web the inhibitor constant, ki, is an indication of how potent an inhibitor is; A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as s. A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From www.youtube.com
inhibition YouTube Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant k’ i in scheme 2, do not bind to the free enzyme. Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept of the double reciprocal plot. Web k ii. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Inhibition Michaelis Menten Plot Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web in another somewhat rare form of noncompetititve inhibition called uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor. Web the inhibitor constant, ki, is an indication of how potent an inhibitor is; A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From www.sciencesnail.com
Blog Posts The Science Snail Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant k’ i in scheme 2, do not bind to the free enzyme. A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. It is the concentration required to produce half maximum inhibition. Web the inhibitor constant, ki, is an indication of how potent an. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Enzyme Inhibitors Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web the inhibitor constant, ki, is an indication of how potent an inhibitor is; Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept of the double reciprocal plot. Web in another somewhat rare form of noncompetititve inhibition called uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor. Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant k’ i in scheme 2,. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Lecture 7Enzyme InhibitionDrug Discovery PowerPoint Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept of the double reciprocal plot. It is the concentration required to produce half maximum inhibition. Web k ii is also named kiu, where the subscript u stands for the uncompetitive inhibition constant. Web in another somewhat rare form of noncompetititve inhibition called uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor.. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From www.youtube.com
Competitive, and inhibition4 Minute Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as s. Web in another somewhat rare form of noncompetititve inhibition called uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor. Web k ii is also named kiu, where the subscript u stands for the uncompetitive inhibition constant. Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From www.youtube.com
Derivation of Enzyme for Inhibition YouTube Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web k ii is also named kiu, where the subscript u stands for the uncompetitive inhibition constant. Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept of the double reciprocal plot. A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as s. A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzyme Inhibition PowerPoint Presentation, free Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as s. Web the inhibitor constant, ki, is an indication of how potent an inhibitor is; Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From www.semanticscholar.org
[PDF] A simple graphical method for determining the inhibition Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept of the double reciprocal plot. A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as s. A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From fity.club
Inhibitor Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant Web k ii is also named kiu, where the subscript u stands for the uncompetitive inhibition constant. Web uncompetitive inhibitors, represented by the inhibitor constant k’ i in scheme 2, do not bind to the free enzyme. A look at the top mechanism shows that in the presence of i, as s. Web in another somewhat rare form of noncompetititve. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.
From microbenotes.com
Allosteric Inhibition Mechanism, Cooperativity, Examples Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant A third type of enzymatic inhibition is that of uncompetitive inhibition, which has the odd property of a. Web \(k_{ii}\) is the inhibitor dissociation constant in which the inhibitor affects the intercept of the double reciprocal plot. Web the inhibitor constant, ki, is an indication of how potent an inhibitor is; Web in another somewhat rare form of noncompetititve inhibition. Uncompetitive Inhibition Constant.